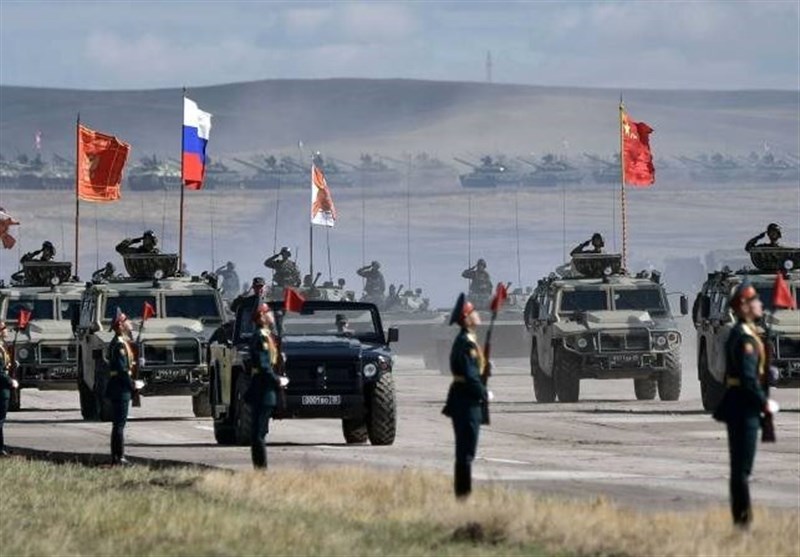
Even though the two countries have held several bilateral and multilateral joint military drills in the past two decades, the quality and dimensions of such drills are gradually expanding and becoming sophisticated. Notwithstanding, the recent military maneuver between Russia and China codenamed “Zapad/Interaction-2021” which began on Monday 09 August 2021 in Ningxia Hui in northwestern China cannot be assessed without attention to the status quo of relations between Moscow and Beijing.
A review of the recent year’s relations between China and Moscow indicates that 2014 is a turning point in bilateral relations. The crisis of Ukraine which was accompanied by various pressures by the West against Russia, guided Moscow to find a reliable partner in the East. Even though the leaders of Russia were aware of the long-term challenges in their relations with China, proximity with Beijing would provide an appropriate tool for this country to confront European and American countries. At least, in the energy dimension, China would provide a proper alternative market for this country.
However, these relations were not limited solely to the energy sector but also included numerous economic and military areas. In 2018, bilateral trade between Russia and China reached about 100 billion dollars and in the military sector, cooperation between the two included various dimensions such as the selling of weapons, holding joint military exercises, nuclear cooperation and other issues.
On the other hand, Beijing put on its foreign policy agenda the expansion of relations with Moscow for many strategic, military and economic reasons. This expansion of relations has become more critical for Beijing with the escalation of tension with the United States.
On such a basis, the recent military drill should be viewed within the framework of expansion of cooperation in the military sector. Holing military wargames is on one hand suggestive of the level of mutual trust between the two sides and on the other, presents a warning to the common threats of the two countries. The number of joint military drills of the two countries in recent years is well demonstrative of the will of the parties to expand military cooperation and coordination.
Notwithstanding, confrontation with probable threats of the two countries is another motivator of China and Russia in holding military drills. Under the present circumstances, especially after the withdrawal of the US from Afghanistan, uncertainty towards future of the Central and Southern Asia regions is the common concern of the Chinese and Russian leaders. Like the counter-terrorism mechanism of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, Moscow and Beijing have serious determination for demonstrating their ability to precent a common security commodity. Until recently, it was imagined that the US is responsible for that. In the same manner, the introduction and presentation of the self as a responsible activist would be a result of cooperation in line with strengthening stability and combating insecurity in this region.
In addition to the above issues, the role of the United States in the recent reservations of relations between Moscow and Beijing should not be ignored. Following the meeting between Joe Biden and Vladimir Putin in June, numerous discussions were made in academic and policy making circles concerning that the United States is seeking the advancement of the policy of détente with Russia in order to make it distant from China. Following this meeting, the Chinese officials emphasized stability in their relations with Russia and after that, the two sides renewed the strategic, friendship and cooperation participation agreement. Under such conditions, holding a joint military drill could be considered as China’s determination to expand relations with Russia and of course a warning to the US that China’s relations with Russia are inviolable.
There are several outstanding features about the recent military maneuver which makes it distinguishable from the previous military drills: this joint military drill was the first joint exercise hosted by China after the outbreak of Covid-19. Moreover, in this drill, the military forces of Russia participating in the drills used some of the equipment of the China’s Army. In the military drill of 2020 in the Caucasus, for the first time, the Russian military equipment and arms were used by the participating military forces of China. One of the other outstanding features of the recent military drill was the presence of some advanced weaponry of China such as the G-20 fighter jets.
In addition to China, Russia has a lot of motivation too to join common military drills with China due to the lack of trust to Western policies. Moreover, holding joint military drills in the highest level of use of weapons could provide Moscow with this opportunity that even in view of the efforts of the West to deescalate tensions, it can exploit the expansion of its relations with Beijing as a tool to exert pressure on the West and or gain more concessions.
In conclusion, the recent military drill demonstrates the effort of China and Russia to enhance cooperation in confronting common threats which could be created in the coming months or years in the region. It also sends a serious signal to their systemic rival ie the United States, In sum, the two parties enjoy sufficient motivation to maintain the present progressive trend which has been the main feature of their relations in the past several years.









0 Comments